The ground state of hydrogen is nondegenerate, so the first-order correction to the ground state energy is given by
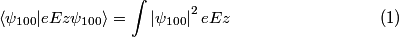 where we have taken the electric field to be in the positive  direction for convenience. Recall the function form of the ground state of hydrogen direction for convenience. Recall the function form of the ground state of hydrogen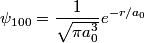 This function is symmetric about the x-y plane (i.e. 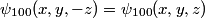 ). Therefore, the integral in equation (1) must be zero, because ). Therefore, the integral in equation (1) must be zero, because  is antisymmetric with respect to the x-y plane, so the is antisymmetric with respect to the x-y plane, so the  integral will be an integral of an odd function over the symmetric interval integral will be an integral of an odd function over the symmetric interval 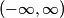 . Therefore, answer (A) is correct. . Therefore, answer (A) is correct. |